

OWASP Top Ten 2013 Category A2 - Broken Authentication and Session Management OWASP Top Ten 2004 Category A3 - Broken Authentication and Session Management
#Session fixation attack code#
The following example shows a snippet of code from a J2EE web application where the application authenticates users with a direct post to the j_security_check, which typically does not invalidate the existing session before processing the login request.Ĭategory - a CWE entry that contains a set of other entries that share a common characteristic.
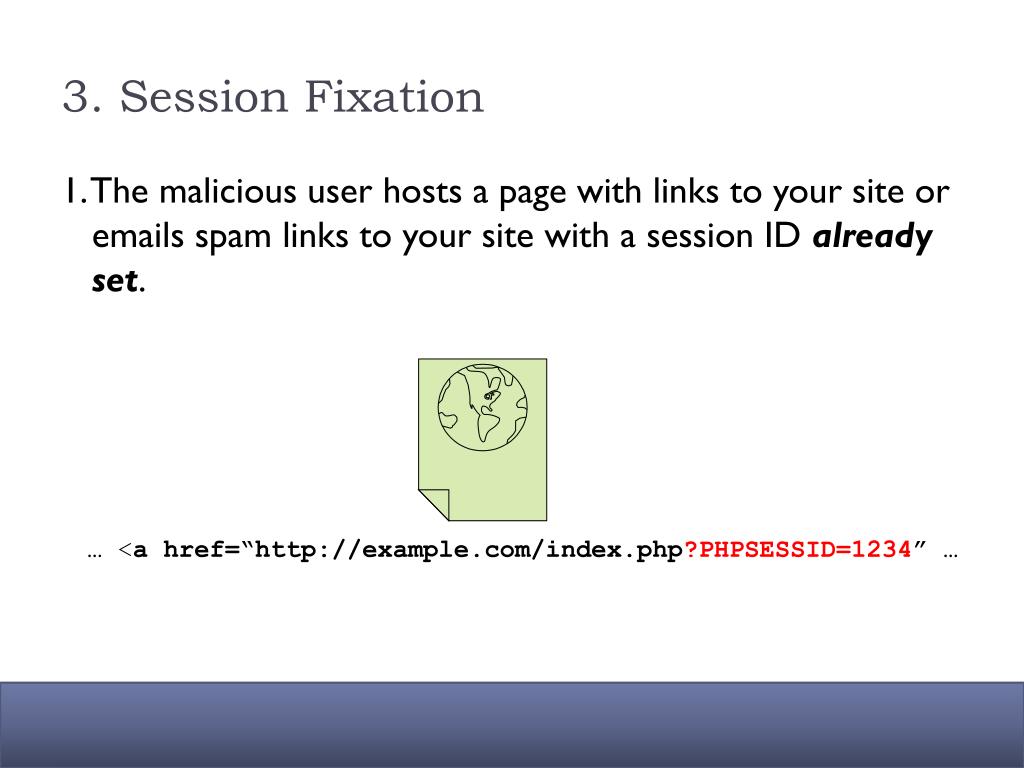
If multiple applications reside on the same top level domain, such as and, a vulnerability in one application can allow an attacker to set a cookie with a fixed session identifier that will be used in all interactions with any application on the domain. It is worth noting that cookies are often tied to the top level domain associated with a given URL.

By tricking the victim into submitting a malicious request to a vulnerable application that reflects JavaScript or other code back to the victim's browser, an attacker can create a cookie that will cause the victim to reuse a session identifier controlled by the attacker. The most common technique employed by attackers involves taking advantage of cross-site scripting or HTTP response splitting vulnerabilities in the target site. However, do not be lulled into complacency attackers have many tools in their belts that help bypass the limitations of this attack vector. In the example above, the attacker did this through a direct method that is not subtle and does not scale suitably for attacks involving less well-known web sites. The biggest challenge an attacker faces in exploiting session fixation vulnerabilities is inducing victims to authenticate against the vulnerable application using a session identifier known to the attacker. The less well known the site is, the lower the odds of an interested victim using the public terminal and the lower the chance of success for the attack vector described above. Finding a victim who is both using a public terminal and interested in logging into the vulnerable application is possible as well, so long as the site is reasonably popular. In most circumstances, the first two challenges are surmountable given a sufficient investment of time. Even given a vulnerable application, the success of the specific attack described here is dependent on several factors working in the favor of the attacker: access to an unmonitored public terminal, the ability to keep the compromised session active and a victim interested in logging into the vulnerable application on the public terminal. The code responsible for authenticating the victim continues to use the pre-existing session identifier, now the attacker simply uses the session identifier recorded earlier to access the victim's active session, providing nearly unrestricted access to the victim's account for the lifetime of the session. Next, a victim sits down at the same public terminal, notices the browser open to the login page of the site, and enters credentials to authenticate against the application. In order to exploit the code above, an attacker could first create a session (perhaps by logging into the application) from a public terminal, record the session identifier assigned by the application, and reset the browser to the login page. Unintended Proxy or Intermediary ('Confused Deputy') Base level weaknesses typically describe issues in terms of 2 or 3 of the following dimensions: behavior, property, technology, language, and resource.Įxternal Control of Assumed-Immutable Web Parameter That is still mostly independent of a resource or technology, but with sufficient details to provide specific methods for detection and prevention. Class level weaknesses typically describe issues in terms of 1 or 2 of the following dimensions: behavior, property, and resource.
More specific than a Pillar Weakness, but more general than a Base Weakness. Class - a weakness that is described in a very abstract fashion, typically independent of any specific language or technology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
